
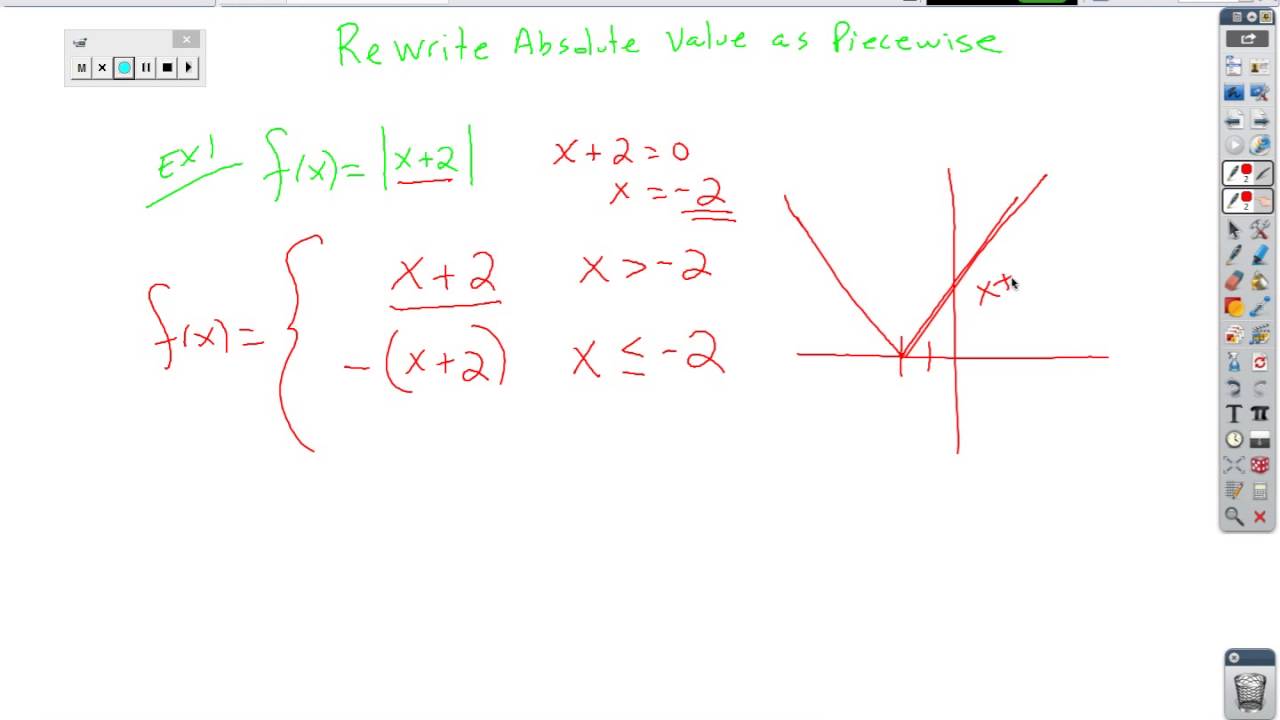
Here you are given a graph that shows the function for absolute value, p( x) = | x| − 4 and asked to graph q( x). Given the graph of the function p( x) = | x| − 4, graph the function q( x) = − p( x) + 2. With that in mind, let’s try a couple of questions! In all other aspects, however, you will treat the absolute value function as you would any other function. Even when manipulated through shifting or compressing, the symmetry of the absolute value graph will remain intact. You should also note that the absolute value graph is symmetrical. Whenever you encounter a graph that adheres to the V-shape, you are dealing with absolute value. One of the key features of the absolute value graph is the “V” shape, which occurs because the absolute value is the distance from zero and, therefore, does not fall below the zero value on the y-axis. For example, |4| = 4, |−4| = 4, and |−222| = 222.īecause the absolute value of any number is positive, the graph of f( x) = | x|, shown in the following figure, has a domain of all real numbers but a range of all real numbers greater than or equal to zero. Thus, the absolute value of any number is positive. You should recall that the absolute value of a number is its distance from zero. (After all, you never know when you’ll need to compare functions to determine the perfect acceleration rate for catapulting pumpkins at the annual Pumpkin-Chucking Contest.)įirst we’ll talk a little bit about absolute value. Finally, we will wrap up the chapter by discussing functions in the real world.

Then we’ll learn about inverse functions and the horizontal line test. In this chapter, we’ll cover some special types of functions that you will probably be introduced to toward the end of your Algebra I course. Up until this point, the functions we’ve worked with have closely resembled the equations and expressions we worked with in the first section of this book. finding the domain and range of functions.function transformations, including translations, reflections, stretches, and compressions.the standard and vertex forms of quadratic equations and functions.solving and graphing exponential equations.solving and graphing quadratic equations and functions.solving and graphing linear equations and functions.Absolute Value, Piecewise, and Step Functionsīefore beginning this chapter, you should be familiar with: Explain the purpose of the horizontal line test Lesson 10.1.Determine, identify, and graph inverse functions.Determine whether a function is continuous or discontinuous.Graph and manipulate absolute value, step, and piecewise functions.Identify absolute value, step, and piecewise functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
